In the previous post, we looked at an overview of the TLM 1 classes. This post will give you a sample code using some of the TLM 1 classes.
Components
We created the following components to demonstrate different kinds of TLM 1 interface. The jelly_bean_sequencer (the leftmost component) creates an object of the jelly_bean_transaction, called jb_req. The jb_req is transferred all the way to the right (jelly_bean_transporter) via several TLM 1 interfaces. The jelly_bean_transporter evaluates the flavor of the jb_req and returns another jelly_bean_transaction called jb_rsp (jelly-bean response) with the updated taste property. The jb_rsp is transferred back to the jelly_bean_subscriber at the end. Though this example is artificial, it will show you a variety of TLM 1 interfaces.
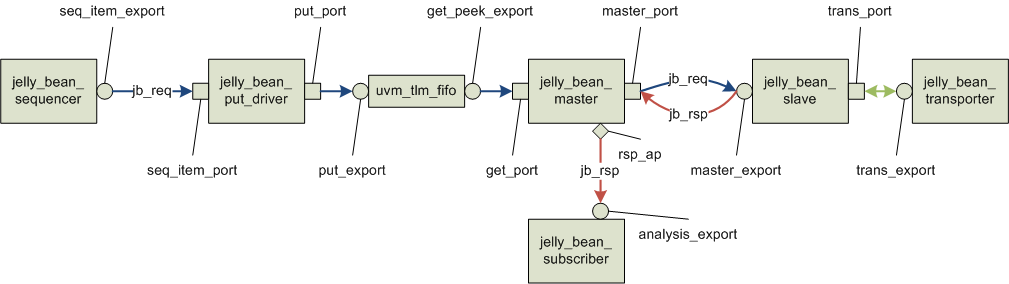
jelly_bean_sequencer
The jelly_bean_sequencer is a uvm_sequencer specialized with the jelly_bean_transaction.
typedef uvm_sequencer#(jelly_bean_transaction) jelly_bean_sequencer; |
jelly_bean_put_driver
The jelly_bean_put_driver is a uvm_driver, which means it has a seq_item_port. The line 4 declares another port (put_port). The run_phase gets a jb_req from the seq_item_port (line 19) then puts it to the put_port (line 21).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | class jelly_bean_put_driver extends uvm_driver#( jelly_bean_transaction ); `uvm_component_utils( jelly_bean_put_driver ) uvm_put_port#( jelly_bean_transaction ) put_port; function new( string name, uvm_component parent ); super.new( name, parent ); endfunction: new function void build_phase( uvm_phase phase ); super.build_phase( phase ); put_port = new( .name( "put_port" ), .parent( this ) ); endfunction: build_phase task run_phase( uvm_phase phase ); jelly_bean_transaction jb_req; forever begin seq_item_port.get_next_item( jb_req ); `uvm_info( get_type_name(), "[seq_item_port]-->{jb_req}-->[put_port]", UVM_NONE ) put_port.put( jb_req ); seq_item_port.item_done(); end endtask: run_phase endclass: jelly_bean_put_driver |
jelly_bean_master
The jelly_bean_master has one uvm_get_port (get_port, line 4), one uvm_master_port (master_port, lines 5 and 6), and one uvm_analysis_port (rsp_ap, line 7). The run_phase gets a jb_req from the get_port (line 25), then puts it to the master_port (line 27). The jelly_bean_master waits for a jelly-bean response (jb_rsp, line 29), then writes it to the rsp_ap (line 31).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | class jelly_bean_master extends uvm_component; `uvm_component_utils( jelly_bean_master ) uvm_get_port#( jelly_bean_transaction ) get_port; uvm_master_port#( .REQ( jelly_bean_transaction ), .RSP( jelly_bean_transaction ) ) master_port; uvm_analysis_port#( jelly_bean_transaction ) rsp_ap; function new( string name, uvm_component parent ); super.new( name, parent ); endfunction: new function void build_phase( uvm_phase phase ); super.build_phase( phase ); get_port = new( .name( "get_port" ), .parent( this ) ); master_port = new( .name( "master_port" ), .parent( this ) ); rsp_ap = new( .name( "rsp_ap" ), .parent( this ) ); endfunction: build_phase task run_phase( uvm_phase phase ); jelly_bean_transaction jb_req; jelly_bean_transaction jb_rsp; forever begin get_port.get( jb_req ); `uvm_info( get_type_name(), "[get_port]-->{jb_req}-->[master_port]", UVM_NONE ) master_port.put( jb_req ); `uvm_info( get_type_name(), "{jb_rsp}< --[master_port]", UVM_NONE ) master_port.get( jb_rsp ); `uvm_info( get_type_name(), "{jb_rsp}-->[rsp_ap]", UVM_NONE ) rsp_ap.write( jb_rsp ); end endtask: run_phase endclass: jelly_bean_master |
jelly_bean_slave
The jelly_bean_slave has one uvm_master_imp (master_export, lines 4 to 6), and one uvm_transport_port (trans_port, lines 7 and 8). The jelly_bean_slave also has two queues; the req_q stores the jb_reqs and the rsp_q stores the jb_rsps. The jelly_bean_slave implements the access methods of a uvm_master_imp; namely put, try_put, can_put, get, try_get, can_get, peek, try_peek, and can_peek (lines 34 to 81). The run_phase gets a jb_req from the req_q if available, then calls transport of the trans_port (line 28).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 | class jelly_bean_slave extends uvm_component; `uvm_component_utils( jelly_bean_slave ) uvm_master_imp#( .REQ( jelly_bean_transaction ), .RSP( jelly_bean_transaction ), .IMP( jelly_bean_slave ) ) master_export; uvm_transport_port#( .REQ( jelly_bean_transaction ), .RSP( jelly_bean_transaction ) ) trans_port; jelly_bean_transaction req_q[$]; jelly_bean_transaction rsp_q[$]; function new( string name, uvm_component parent ); super.new( name, parent ); endfunction: new function void build_phase( uvm_phase phase ); super.build_phase( phase ); master_export = new( "master_export", this ); trans_port = new( .name( "trans_port" ), .parent( this ) ); endfunction: build_phase task run_phase( uvm_phase phase ); jelly_bean_transaction jb_rsp; forever begin wait ( req_q.size() > 0 ); `uvm_info( get_type_name(), "(master_export)---{jb_req}-->[trans_port]", UVM_NONE ) trans_port.transport( req_q.pop_front(), jb_rsp ); `uvm_info( get_type_name(), "{jb_rsp}< --[trans_port]", UVM_NONE ) rsp_q.push_back( jb_rsp ); end endtask: run_phase virtual task put( input jelly_bean_transaction t ); req_q.push_back( t ); endtask: put virtual function bit try_put( input jelly_bean_transaction t ); req_q.push_back( t ); return 1; endfunction: try_put virtual function bit can_put(); return 1; endfunction: can_put virtual task get( output jelly_bean_transaction t ); wait ( rsp_q.size() > 0 ); t = rsp_q.pop_front(); endtask: get virtual function bit try_get( output jelly_bean_transaction t ); if ( rsp_q.size() > 0 ) begin t = rsp_q.pop_front(); return 1; end else begin return 0; end endfunction: try_get virtual function bit can_get(); return rsp_q.size() > 0; endfunction: can_get virtual task peek( output jelly_bean_transaction t ); wait ( rsp_q.size() > 0 ); t = rsp_q[0]; endtask: peek virtual function bit try_peek( output jelly_bean_transaction t ); if ( rsp_q.size() > 0 ) begin t = rsp_q[0]; return 1; end else begin return 0; end endfunction: try_peek virtual function bit can_peek(); return rsp_q.size() > 0; endfunction: can_peek endclass: jelly_bean_slave |
jelly_bean_transporter
The jelly_bean_transporter has one uvm_transport_imp (trans_export, lines 4 to 6) and implements its access methods; namely transport and nb_transport (lines 17 to 32). These methods create a jelly-bean response (jb_rsp, line 24), evaluate the flavor of a jelly-bean request and update the taste property of the jb_rsp accordingly (lines 26 to 29).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | class jelly_bean_transporter extends uvm_component; `uvm_component_utils( jelly_bean_transporter ) uvm_transport_imp#( .REQ( jelly_bean_transaction ), .RSP( jelly_bean_transaction ), .IMP( jelly_bean_transporter ) ) trans_export; function new( string name, uvm_component parent ); super.new( name, parent ); endfunction: new function void build_phase( uvm_phase phase ); super.build_phase( phase ); trans_export = new( "trans_export", this ); endfunction: build_phase virtual task transport( input jelly_bean_transaction jb_req, output jelly_bean_transaction jb_rsp ); assert( nb_transport( jb_req, jb_rsp ) ); endtask: transport virtual function bit nb_transport( input jelly_bean_transaction jb_req, output jelly_bean_transaction jb_rsp ); jb_rsp = jelly_bean_transaction::type_id::create( "jb_rsp" ); jb_rsp.copy( jb_req ); if ( jb_req.flavor == jelly_bean_transaction::CHOCOLATE && jb_req.sour ) jb_rsp.taste = jelly_bean_transaction::YUCKY; else jb_rsp.taste = jelly_bean_transaction::YUMMY; `uvm_info( get_type_name(), { "Returning:\n", jb_rsp.sprint() }, UVM_NONE ) return 1; endfunction: nb_transport endclass: jelly_bean_transporter |
jelly_bean_subscriber
The jelly_bean_subscriber is a uvm_subscriber, which means it has an analysis_export. The jelly_bean_subscriber implements the write method of the analysis_export (lines 8 to 10).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | class jelly_bean_subscriber extends uvm_subscriber#( jelly_bean_transaction ); `uvm_component_utils( jelly_bean_subscriber ) function new( string name, uvm_component parent ); super.new( name, parent ); endfunction: new function void write( jelly_bean_transaction t ); `uvm_info( get_type_name(), { "Received:\n", t.sprint() }, UVM_NONE ) endfunction: writeendclass: jelly_bean_subscriber |
jelly_bean_agent
The jelly_bean_agent instantiates all the components and connect them together.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 | class jelly_bean_agent extends uvm_agent; `uvm_component_utils( jelly_bean_agent ) jelly_bean_sequencer jb_seqr; jelly_bean_put_driver jb_put_drvr; uvm_tlm_fifo#( jelly_bean_transaction ) jb_fifo; jelly_bean_master jb_master; jelly_bean_slave jb_slave; jelly_bean_transporter jb_trans; jelly_bean_subscriber jb_sub; function new( string name, uvm_component parent ); super.new( name, parent ); endfunction: new function void build_phase( uvm_phase phase ); super.build_phase( phase ); jb_seqr = jelly_bean_sequencer ::type_id::create( .name( "jb_seqr" ), .parent( this ) ); jb_put_drvr = jelly_bean_put_driver ::type_id::create( .name( "jb_put_drvr" ), .parent( this ) ); jb_fifo = new( .name( "jb_fifo" ), .parent( this ) ); jb_master = jelly_bean_master ::type_id::create( .name( "jb_master" ), .parent( this ) ); jb_slave = jelly_bean_slave ::type_id::create( .name( "jb_slave" ), .parent( this ) ); jb_trans = jelly_bean_transporter::type_id::create( .name( "jb_trans" ), .parent( this ) ); jb_sub = jelly_bean_subscriber ::type_id::create( .name( "jb_sub" ), .parent( this ) ); endfunction: build_phase function void connect_phase( uvm_phase phase ); super.connect_phase( phase ); jb_put_drvr.seq_item_port.connect( jb_seqr.seq_item_export ); jb_put_drvr. put_port.connect( jb_fifo.put_export ); jb_master. get_port.connect( jb_fifo.get_peek_export ); jb_master. master_port.connect( jb_slave.master_export ); jb_slave. trans_port.connect( jb_trans.trans_export ); jb_master. rsp_ap.connect( jb_sub.analysis_export ); endfunction: connect_phase endclass: jelly_bean_agent |
Simulation
Here is an excerpt of a simulation output.
# UVM_INFO ../src/tutorial_20.sv(118) @ 0: uvm_test_top.jb_env.jb_agent.jb_seqr@@jb_seq [one_jelly_bean_sequence] Generated: # UVM_INFO ../src/tutorial_20.sv(152) @ 0: uvm_test_top.jb_env.jb_agent.jb_put_drvr [jelly_bean_put_driver] [seq_item_port]-->{jb_req}-->[put_port] # UVM_INFO ../src/tutorial_20.sv(188) @ 0: uvm_test_top.jb_env.jb_agent.jb_master [jelly_bean_master] [get_port]-->{jb_req}-->[master_port] # UVM_INFO ../src/tutorial_20.sv(223) @ 0: uvm_test_top.jb_env.jb_agent.jb_slave [jelly_bean_slave] (master_export)---{jb_req}-->[trans_port] # UVM_INFO ../src/tutorial_20.sv(282) @ 0: uvm_test_top.jb_env.jb_agent.jb_trans [jelly_bean_transporter] Returning: # UVM_INFO ../src/tutorial_20.sv(225) @ 0: uvm_test_top.jb_env.jb_agent.jb_slave [jelly_bean_slave] {jb_rsp}< --[trans_port] # UVM_INFO ../src/tutorial_20.sv(190) @ 0: uvm_test_top.jb_env.jb_agent.jb_master [jelly_bean_master] {jb_rsp}<--[master_port] # UVM_INFO ../src/tutorial_20.sv(192) @ 0: uvm_test_top.jb_env.jb_agent.jb_master [jelly_bean_master] {jb_rsp}-->[rsp_ap] # UVM_INFO ../src/tutorial_20.sv(298) @ 0: uvm_test_top.jb_env.jb_agent.jb_sub [jelly_bean_subscriber] Received: |
I hope this tutorial helped you to understand the TLM 1 interfaces.
Hi Keisuke:
great Tutorial and very helpful.
Is there any possibility to post anything about callback, like recommand usage, work mode etc, very appreciated
Thanks. Pan
Thanks for the comment. UVM does provide a callback mechanism, but it is not recommended to use due to a performance impact. I would suggest to use the UVM factory to override a class instead of using a callback.
Hi Keisuke,
Whats the difference between imp and export ?? Practical use of each of them ?? Thanks in advance………
Hi Vittal,
Please see this discussion. Let me know if you have further questions.
Thanks for the tutorial. I have what I need now to build a very powerful environment for data cache verification.
In your example, you connect get_peek_export to get_port (not get_peek_port) from uvm_tlm_fifo to jelly_bean_master. Is it because get_port is just a subset of get_peek_port, that is why we can use get_port here?
That’s right. While
get_peek_exportimplementsget,try_get,can_get,peek,try_peek, andcan_peek,get_portimplementsget,try_get, andcan_getonly. Since all the methods the consumer (jelly_bean_master) can call via itsget_portare supported by theget_peek_export, you can connect them together.Hi Keisuke,
I noticed that when you implement the access methods of a uvm_master_imp in jelly_bean_slave, some methods you use functions to realize, some methords you use tasks, for example, the put method you use task, while the try_put method you use function.
I wonder to know why you choose task on some methods and funciton on others?
Thanks,
Rui
Whether to use function or task is defined by the
uvm_tlm_if_baseclass which is the super class of theuvm_master_impclass.